
Many infections do not cause symptoms in healthy people.The immune system suppresses the activity of the virus, which results in a human being a carrier of infection.At the same time, the spread of pathogens is even a complete clinical well, as the viral particles are in the patient's biological fluids.The hidden course of the infection can be the main cause of the significant spread of the disease: patients do not participate in time and unconsciously continue to infect other people.
The human papilloma virus (HPV) is an excellent example of a hidden infectious agent.Most people are infected with at least one type of HPV throughout their lives, but the clinical manifestations of the disease do not always occur.Doctors attribute an increased risk of developing malignant tumors to distant complications of infection.In fact, patients with immune deficiency often have such negative consequences of the disease.The topic drugs help suppress the symptoms of HPV infection.Time vaccination is also recommended.
More information about the illness
The human papilloma virus is a pathogen of infection that affects the skin and mucous membranes of the organs.The main manifestation of the disease is the growth of tumors in the person's area, the oral cavity and the throat.In some cases, pointed papillomas are formed in non -specific places, such as the lower and upper limbs.The localization of warts depends on the type of HPV.In most people, infection leads to hidden transport of infection, but with a decrease in immunity, the virus shows its virulence.In some cases, immune competent cells destroy the pathogen independently within 3-6 months after invasion of the body.
HPV infection is the most common sexually transmitted disease.Such an indicator can be explained by the high virulence of the virus and the asymptomatic pathology of most people.The use of condoms does not always avoid the infection, so the patient can continue to spread the virus with protected sexual relationships.At the same time, experts have developed effective vaccinations that prevent the formation of HPV oncogene.Immunization is presented in adolescence by girls because the protection against virus should be involved before the first sexual contact.
The characteristics of the virus
Human papilloma virus is a DNA-containing pathogen.Unlike bacteria and other microorganisms, viruses can only show their activity after introducing it into the cage and embedding their own genetic information into the seed.Subsequently, the affected cell begins to synthesize the proteins needed to assemble the virus particles.Almost every representative of the papillomavirus family attacks only one type of organization, and HPV infection can only occur in people.
Scientists know more than 600 human papilloma virus strains (types) distinguished by genetic information.40 types of HPV are caused by various forms of mucosa and skin damage.At the same time, classification of the degree of oncogenicity of strains is of important clinical importance.Thus, women's cervical cancer is most common with HPV invasions of 16 and 18.These infectious agents are not always presented by skin changes.
HPV strikes in the base layer of the epithelium.The pathogen can exist in an episode that is not associated with cell DNA or in an integrated form related to cell genoma.The integrated virus produces the necessary proteins and causes clinical manifestations of the disease.HPV's life in the body is not a direct cause of malignant tissue degeneration, but carrying the virus increases the risk of cancer risk factors.
Infection methods
The virus is found in basic epithelial cells, so any microtrauma of the skin and mucous membrane increases the risk of infection.In most cases, HPV is covered with vaginal, anal or oral sexual contact.The condom can only be provided with the surface of the skin, but the virus particles can continue to penetrate the body through other coverings.The presence of gender warts is prone to the spread of the pathogen, but the skin outside the carrier of the disease is also a source of HPV.
Other transmission roads
- Infection of the child during childbirth.Children are most commonly defeated by the respiratory tract
- Independent transfer of a virus from one part of the body to another
- Personal hygiene articles including razors, toothbrushes and towels, general use
- Blood transfusion.Recent studies have confirmed the possibility of transfusion infection.
- Surgical interventions in non -sterile conditions
Despite the various causes of the viral invasion, only the sexual path of HPV infection is clinical.Other sources of infection are characterized by the low risk of the pathogen.
Risk factors
In addition to the direct ways to transmit HPV, the role of risk factors should also be taken into account.We are talking about the characteristics of human lifestyle and certain physical conditions.
The most important risk factors of infection
- Many sexual partners.Even with safe sex, active sex life will sooner or later lead to infection.
- Circle.Gender warts are detected in most cases in adolescents and young patients, while the oral cavity and respiratory condylomes are characterized by children.
- Weakened immune system.Patients with HIV infection or acquired immune deficiency severely risk invasion of the virus.In addition, HPV is more often symptomatic after transplantation of the organs.
- Damage to the skin and mucosa.Microtraumas facilitate the penetration of the virus into the base layer of the epithelium.
- Smoking and alcoholism.Bad habits weaken the activity of immunity.
- Vatate infections.
In addition, pregnant women are incorporated into the risk of infection.It should be recalled that prone factors to eliminate the disease are an effective preventive tactic.
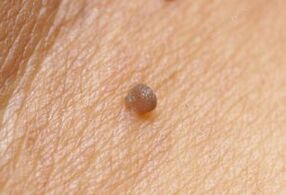
Clinical current
The incubation period that precedes the symptomatic manifestations of the disease may last for several months.In immunocomplete patients, the body can kill the infection at this time, but spontaneous elimination of the pathogen does not always occur.People can simultaneously infect with several tribes of the virus.Signs of HPV infection occur when exposed to harmful factors that weaken tissues.Due to the recurring course, the condyloma regularly disappears and is re -formed.Oncological complications of infections can develop for decades.
Possible consequences of illness:
- Cervical carcinoma - malignant tumor of the epithelial tissue.This type of oncology is only related to the human papilloma virus.By time vaccination, the risk of oncogenesis is reduced.
- The anal hole is a plant -cell carcinoma.Such a complication can occur in men and women.Early symptoms of anus cancer include bleeding and itching of the skin.
- Condyloma urinating is a violation of urinary obstruction.
- Malicious rebirth of warts in the throat and oral cavity.
Cervical cancer is one of the most common causes of women's death.Because this disease involves viral virals, a regular examination is required for a gynecologist.Modern vaccinations protect women from most HPV's oncogenic types.
Diagnosis
Gynecologists, urologists, venereologists and dermatologists are involved in the Condil study.During the initial appointment, the doctor asks the patient about complaints, collects anamnic data and perform skin formations.Usually, HPV manifestations can be easily identified, but other diseases should be excluded.For this, the specialist will prescribe instrumental and laboratory research.
The Diagnostic Methods Required:
- Instrumental examination of the vagina and cervoscopy (colposcopy).Such an examination is necessarily performed to filter cervical carcinoma.During the examination, your doctor may detect multiple papillomas and epithelial dysplasia.
- Biopsy - acquisition of tissue material on changes in the skin or mucous membrane.Cytological examination of the sample allows the identification of malignant cells.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction - Detection of HPV virus particles in the body.Performing the test allows the doctor to determine the pathogen strain and the virus load.
- The Digene Test is a high precision detection of DNA of the oncogenic strains of the human papilloma virus.The study is used as a reliable screening.
Drug treatment
Advanced formulations against HPV infection can only eliminate the symptoms of the disease and prevent tissue disorders.Full elimination of the virus is impossible with medication.Oral and current agents are prescribed at high risk of oncogenesis, immune deficiency and other harmful conditions.If the virus does not manifest itself with external changes, usually general preventive measures.
Possible appointments
- Salicylic acid to remove warts.It is not used to process the skin of the face and genitals.
- Creams and ointments containing immunomodulators.
- Podophilo - ointment with cytostatic effect.The use of the drug to the affected skin leads to the destruction of pathogenic elements.
- Trichlooroxic acid for chemical cauterization of general and gender warts.May cause the local part.
The drugs listed should only be used under medical examination.Once the warts have been removed, the HPV infection can be re -manifested and spread even in other areas.
Surgery
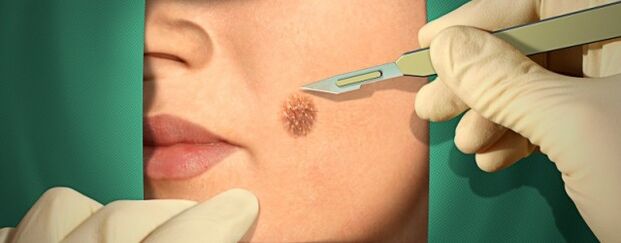
The doctor can offer surgical and minimally invasive methods of patients to remove warts.Such methods usually do not cause complications, but in the first days after the intervention, tissue bleeding may occur.
Types of intervention:
- normal surgical cut;
- Freezing with liquid nitrogen and then destroying the affected tissues;
- Electrical coagulation;
- Removal of papillomas with laser;
- Using a radio wave "knife".
All procedures are performed during local anesthesia.The specialist selects the safest method of treating Condyl.
Forecast
The course of papillomavirus infection depends on the patient's immune system and a specific virus spread.The population is approx.30% of spontaneous elimination of the pathogen caused by active immunity.Symptomically, the disease often occurs in pregnant women, children, elderly people and immune deficiency patients.
HPV infection is characterized by a recurring course.Papillomas formed may gradually disappear or spread to adjacent skin.The oncogenic strains of the virus most often affect the cervical mucosa membrane, and the resulting epithelium improves the effects of the risk factors of malignant tissue degeneration, such as smoking and the use of oral contraceptives.The tumor can form 10-20 years after invasion of the virus into the body.
Prevention
Early immunization is the most reliable method of prevention.Gardaszil vaccination containing viral proteins and complementary components is effective against HPV 6, 11, 16 and 18.If vaccination is carried out early to the first sexual relationship, the risk of later cervical cancer will not exceed 1%.
Further prevention:
- the use of condoms;
- Sexual contact only with reliable partners;
- thorough personal hygiene;
- Gynecological examination at least once a year.























